-
[클린코드] 단위테스트Java/클린코드 2022. 4. 27. 00:20
제로베이스 클린코드 요약 정리 글입니다.
목차
- 테스트 코드의 중요성
- 테스트의 종류
- Unit Test 작성
- FIRST 원칙
1. 테스트 코드의 중요성
- 테스트 코드는 실수를 바로잡아준다.
- 테스트 코드는 반드시 존재해야하며, 실제 코드 못지 않게 중요하다.
- 테스트 케이스는 변경이 쉽도록한다. 코드의 유연성, 유지보수성, 재사용성을 제공하는 버팀목이 단위 테스트이다.
- 테스트 커버리지가 높을수록 버그에 대한 공포가 줄어든다.
- 지저분한 테스트 코드는 테스트를 안하느니만 못하다.
테스트의 중요성
테스트는 실사용에 적합한 설계를 끌어내준다.
테스트를 작성해서 얻게 되는 가장 큰 수확은 테스트 자체가 아니다. 작성 과정에서 얻는 깨달음이다.
테스트는 자동화 되어야 한다.
Build -> Test -> Provide Infrastructure -> Deploy -> Test More
2. 테스트의 종류
Test Pyramid
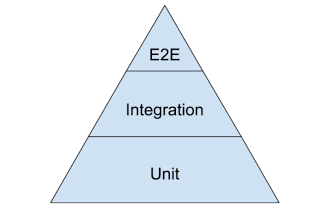
- Unit Test :
- 프로그램 내부의 개별 컴포넌트의 동작을 테스트한다. 배포하기 전에 자동으로 실행되도록 많이 사용한다.
- Integration Test :
- 프로그램 내부의 개별 컴포넌트들을 합쳐서 동작을 테스트한다.
- Unit Test 는 각 컴포넌트를 고립시켜 테스트 하기 때문에 컴포넌트의 interaction 을 확인하는 Integration Test 가 필요하다.
- E2E Test :
- End to End Test. 실제 유저의 시나리오대로 네트워크를 통해 서버의 EndPoint를 호출해 테스트한다.
구글의 제안 : 70% unit tests, 20% integration tests, 10% end-to-end tests
3. Unit Test 작성
테스트 라이브러리를 사용하자
다음은 테스트 라이브러리 종류이다.
- JUnit : for unit test
- Mockito : for mocking dependencies
- Wiremock : for stubbing out external services
- Pact : for writing CDC tests
- Selenium : for writing UI-driven end-to-end tests
- REST-assured : for writing REST API - driven end-to-end tests
실무에서는 JUnit 5 + Mockito 를 많이 사용한다.
Test Double - 테스트에서 원본 객체를 대신하는 객체
- Stub
- 원래의 구현을 최대한 단순한 것으로 대체한다.
- 테스트를 위해 프로그래밍된 항목에만 응답한다.
- Spy
- Stub 의 역할을 하면서 호출에 대한 정보를 기록한다.
- 이메일 서비스에서 메시지가 몇 번 전송되었는지 확인할 때
- Mock
- 행위를 검증하기 위해 가짜 객체를 만들어 테스트하는 방법
- 호출에 대한 동작을 프로그래밍할 수 있다.
- Stub은 상태를 검증하고 Mock 은 행위를 검증한다.
given-when-then 패턴을 사용하자
public void testGetPageHierarchyAsXml() throws Exception { givenPages("PageOne", "PageOne.ChildOne", "PageTwo"); whenRequestIsIssued("root", "type:Pages"); thenResponseShouldBeXML(); } public void testGetPageHierarchyHasRightTags() throws Exception { givenPages("PageOne", "PageOne.ChildOne", "PageTwo"); whenRequestIsIssued("root", "type:pages"); thenResponseShouldContain( "<name>PageOne</name>", "<name>PageTwo</name>", "<name>ChildOne</name>" ); }- given : 테스트에 대한 pre-condition
- when : 테스트하고 싶은 동작 호출
- then : 테스트 결과 확인
Spring Boot Application Test 예제
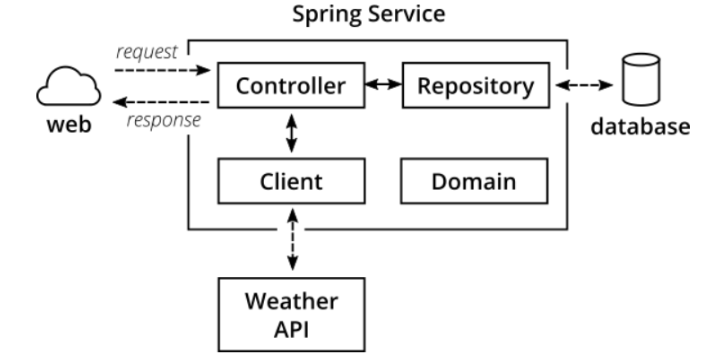
마틴파울러 닷컴 참고 https://martinfowler.com/articles/practical-test-pyramid.html
ExampleController - main 코드
@RestController public class ExampleController { private final PersonRepository personRepo; @Autowired public ExampleController(final PersonRepository personRepo) { this.personRepo = personRepo; } @GetMapping("/hello/{lastName}") public String hello(@PathVariable final String lastName) { Optional<Person> foundPerson = personRepo.findByLastName(lastName); return foundPerson .map(person -> String.format("Hello %s %s!", person.getFirstName(), person.getLastName())) .orElse(String.format("Who is this '%s' you're talking about?", lastName)); } }ExampleController - Unit Test 예시
public class ExampleControllerTest { private ExampleController subject; @Mock private PersonRepository personRepo; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { initMocks(this); subject = new ExampleController(personRepo); } @Test public void shouldReturnFullNameOfAPerson() throws Exception { Person peter = new Person("Peter", "Pan"); given(personRepo.findByLastName("Pan")) .willReturn(Optional.of(peter)); String greeting = subject.hello("Pan"); assertThat(greeting, is("Hello Peter Pan!")); } @Test public void shouldTellIfPersonIsUnknown() throws Exception { given(personRepo.findByLastName(anyString())) .willReturn(Optional.empty()); String greeting = subject.hello("Pan"); assertThat(greeting, is("Who is this 'Pan' you're talking about?")); } }- PersonRepository 는 controller 와 연관된 다른 객체니까 mock 을 사용한다.
- given-when-then 구조
- 사람이 존재할 때와 존재하지 않았을 때 두가지 Test 경우
Integration Test (Database)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @DataJpaTest public class PersonRepositoryIntegrationTest { @Autowired private PersonRepository subject; @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { subject.deleteAll(); } @Test public void shouldSaveAndFetchPerson() throws Exception { Person peter = new Person("Peter", "Pan"); subject.save(peter); Optional<Person> maybePeter = subject.findByLastName("Pan"); assertThat(maybePeter, is(Optional.of(peter))); } }- PersionRepository 가 데이터베이스와 연결될 수 있는지 확인하는 코드
- in-memory DB 인 h2 로 테스트
- findByLastName 가 정상적으로 동작하는지 확인한다.
Integration Test (Service)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class WeatherClientIntegrationTest { @Autowired private WeatherClient subject; @Rule public WireMockRule wireMockRule = new WireMockRule(8089); @Test public void shouldCallWeatherService() throws Exception { wireMockRule.stubFor(get(urlPathEqualTo("/some-test-api-key/53.5511,9.9937")) .willReturn(aResponse() .withBody(FileLoader.read("classpath:weatherApiResponse.json")) .withHeader(CONTENT_TYPE, MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) .withStatus(200))); Optional<WeatherResponse> weatherResponse = subject.fetchWeather(); Optional<WeatherResponse> expectedResponse = Optional.of(new WeatherResponse("Rain")); assertThat(weatherResponse, is(expectedResponse)); } }- 서비스와 Integration Test 를 하는 부분
- 클라이언트가 weather API 라는 외부 API 서버를 호출하는 부분이 정상적인지 테스트
- WireMock 을 이용해 mock 서버를 띄운다.
- client가 실제 서버가 아닌 mock 서버로 요청하게 해서 client 의 동작을 테스트한다.
FIRST 원칙
- Fast : 테스트는 빨리 돌아야 한다.
- Independent : 각 테스트는 서로 독립적
- Repeatable : 테스트는 어떤 환경에서도 반복 가능해야한다.
- Self-Validating : 테스트는 스스로 bool 값을 내야한다.
- Timely : 테스트는 적시에 (실제코드 직전에) 구현한다.
'Java > 클린코드' 카테고리의 다른 글
[클린코드] 경계 (0) 2022.03.02 [클린코드] 오류 처리 (0) 2022.03.01 [클린코드] 객체와 자료구조 (0) 2022.02.23 [클린코드] 형식 맞추기 (0) 2022.02.15 [클린코드] 주석 (0) 2022.02.11